Plastic is an important basic material that can be seen everywhere in our lives, but the pollution caused by non-standard use and disposal can also bring certain pressure to the ecological environment. The relevant work deployment starts from the daily life and daily life of ordinary people, which can enable them to actively participate in plastic pollution control work and contribute to ecological environment protection.
What else can we use after some plastic products are no longer usable? Are these alternative products environmentally friendly?
When we actively participate in plastic pollution control work, some plastic products cannot be used in daily life, but there are still some alternative products that can be used. In places such as supermarkets, pharmacies, and bookstores, we can use eco-friendly cloth bags, paper bags, and other non plastic products as well as biodegradable shopping bags; In dining establishments, we can use straw free beverage cups, biodegradable plastic tableware, bamboo and wood tableware, etc; It will also facilitate our lives.
Like biodegradable plastic products, the main products after degradation are carbon dioxide converted from organic carbon, microbial organic dead bodies, mineralized inorganic salts, etc., which are harmless to the environment; Cloth bags are durable and can be reused multiple times. Paper bags are made of wood and can also be reused multiple times. They are all environmentally friendly bags and are harmless to the environment.

From the perspective of environmental protection, degradable plastics refer to a type of material that can be completely degraded under specific conditions or in the natural environment. That is, in nature, such as soil, sand, compost, anaerobic digestion, or water bodies, it can be ultimately completely degraded into a type of high molecular weight material that is environmentally friendly. The environmentally harmless substances after degradation include carbon dioxide and/or methane, water, mineralized inorganic salts, and new biomass (such as microbial dead bodies). Simply put, degradable plastics refer to plastics that can naturally degrade into pollution-free small molecules in the environment, without causing harm or secondary pollution to the environment. At present, fully biodegradable polymers mainly include PLA, PBAT, PBS, PBSA, PCL, PPC, PGA, PPDO, etc.
The statement that biodegradable plastics can only degrade under composting conditions is incorrect. Due to different varieties and chemical structures, the degradation process of biodegradable plastics varies under different conditions. Composting is just one of the conditions under which it can degrade. Most biodegradable plastics will degrade in natural environments such as soil, fresh water, or seawater under suitable temperature and humidity conditions, and ultimately be completely decomposed by microorganisms into environmentally friendly substances. Materials such as PBAT, PCL, PHA, etc. can be completely degraded within a maximum of six months under suitable conditions such as composting, soil, and seawater. Although PLA material degrades rapidly under composting conditions and can be completely degraded within six months, it can also degrade in natural environments such as soil and seawater. For example, in the field experiments of PBAT and PLA material biodegradable plastic film conducted in Yunnan, Xinjiang, and other places, the degradation of the plastic film was obvious in the first year of the experiment. In the second year after crop harvesting and soil tillage, the film had already achieved complete degradation. In addition, monomers such as PLA, PBAT, PCL, and PHA can also be chemically recovered and reused through alcoholysis, acid-base degradation, and other methods.
In general, the degradation conditions of degradable plastics include various factors such as light, oxygen, heat, water, biology, and microorganisms. Especially microorganisms, they are essential for the degradation process. The final stage of the degradable process involves the participation of microorganisms in breaking down plastics into small molecules such as carbon dioxide and water, which are environmentally friendly substances. Because the degradation of biodegradable plastics requires certain conditions, especially microorganisms, it will not degrade during daily use, so everyone can use it with confidence.
"Degradable" plastics and "bio based" plastics cannot be equated, the two are completely different concepts. "Degradable" plastics are more from the perspective of environmental pollution control, considering whether materials or products can be completely degraded after being discarded and entering the garbage disposal system or leaking into the environment, and whether they are harmless to the environment or will not cause pollution to the environment. Biobased plastics, on the other hand, rely more on the source of raw materials and utilize renewable resources such as biomass to manufacture materials or products, in order to save the use of fossil resources.
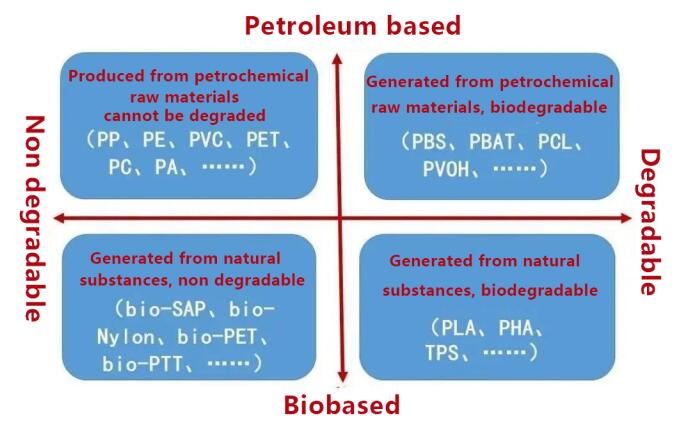
Overall, as shown in the figure below, bio based plastics may not necessarily be degradable, they can be both degradable and non degradable; And degradable plastics may not necessarily be biobased, they can be both biobased and abiotic.
