(Degradation degree, environmental protection effect, application scenarios)
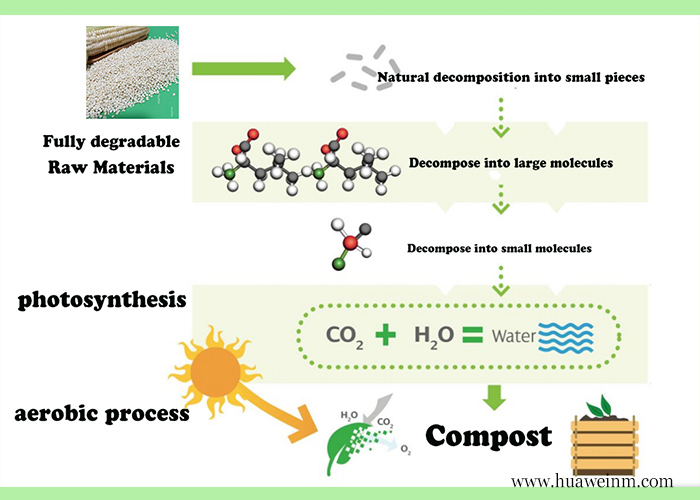
Total degradation refers to materials that can be completely decomposed into harmless substances such as water, carbon dioxide, and biomass through microbial action or chemical reactions under specific conditions. This material can be completely decomposed by microorganisms in the natural environment, ultimately transforming into harmless substances and reducing pollution to the environment. The main sources include corn, calcium carbonate, cassava, etc., which are processed into lactic acid (PLA), which has good biodegradability and ultimately generates carbon dioxide and water without polluting the environment. Fully degradable plastic bags can be completely degraded under specific conditions, usually within 3-6 months under composting conditions (60-70 degrees).
The main components of fully degradable materials include PLA (polylactic acid), PBAT (polybutylene terephthalate), PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoate), etc. These materials can be degraded through the action of microorganisms in nature, such as bacteria, mold, and algae, and ultimately completely decomposed into water and carbon dioxide.
Fully biodegradable materials have a wide range of applications in the field of environmental protection, such as packaging materials, agricultural film, disposable tableware, etc. The use of these materials can significantly reduce the environmental pollution caused by traditional plastics and meet the requirements of sustainable development. The advantage of fully biodegradable materials lies in their environmental friendliness, which allows for rapid degradation in natural environments and reduces pressure on ecosystems.
The development trend of fully degradable materials
With the increasing global awareness of environmental protection, the application prospects of fully biodegradable materials are broad. In the future, with the advancement of technology and the reduction of costs, fully degradable materials are expected to be applied in more fields and become an important means to solve environmental problems. The support of the government and enterprises will also promote the further development and popularization of fully biodegradable materials.
Degradable refers to the characteristic of substances undergoing biological or physical processes in the natural environment, ultimately decomposing into harmless substances that can be fully absorbed or reused by the environment. Degradable materials refer to materials that are thermodynamically and kinetically degradable, mainly including photodegradable materials, biodegradable materials, etc. Degradable plastics refer to the addition of a certain amount of additives (such as starch, modified starch or other cellulose, photosensitizers, biodegradable agents, etc.) during the production process of plastics, making them easier to degrade in the natural environment, but not completely degradable. Degradable plastic bags still need to be buried or incinerated, and cannot undergo specialized industrial composting degradation treatment, which still poses a certain degree of pollution to the environment.
The degradation process of biodegradable materials mainly includes biodegradation, photodegradation, and chemical degradation. Biodegradation refers to the process by which materials are broken down into common forms of compounds in nature, such as carbon dioxide and water, under the action of microorganisms. Photodegradation refers to the breaking of molecular chains in materials under light conditions, ultimately leading to the degradation into small molecules. Chemical degradation is the process of reducing the molecular weight and performance of materials through chemical reactions.
Degradable materials are widely used in various fields, such as agriculture, packaging, healthcare, etc. They can naturally decompose in nature, reducing pollution to the environment. However, the current use of biodegradable plastics is not ideal, and most of them are still burned or buried, with environmental impacts similar to traditional plastics. Therefore, further research and improvement are needed in the preparation and application of biodegradable materials to achieve true environmental goals.

Application scenario: Fully biodegradable plastic bags are considered a more environmentally friendly choice due to their complete degradation characteristics, and are widely used in situations that require complete biodegradation, such as agriculture, food packaging, etc. Degradable plastic bags are mainly used in situations where rapid degradation is required but complete decomposition is not necessary due to incomplete degradation.
Environmental protection effect: Fully degradable plastic bags can be completely degraded under specific conditions without polluting the environment, which is very beneficial for protecting the environment. Although biodegradable plastic bags have added biodegradable components, they still cannot be completely degraded. The disposal method after disposal is similar to traditional plastic bags, and there is still a certain degree of pollution to the environment.
